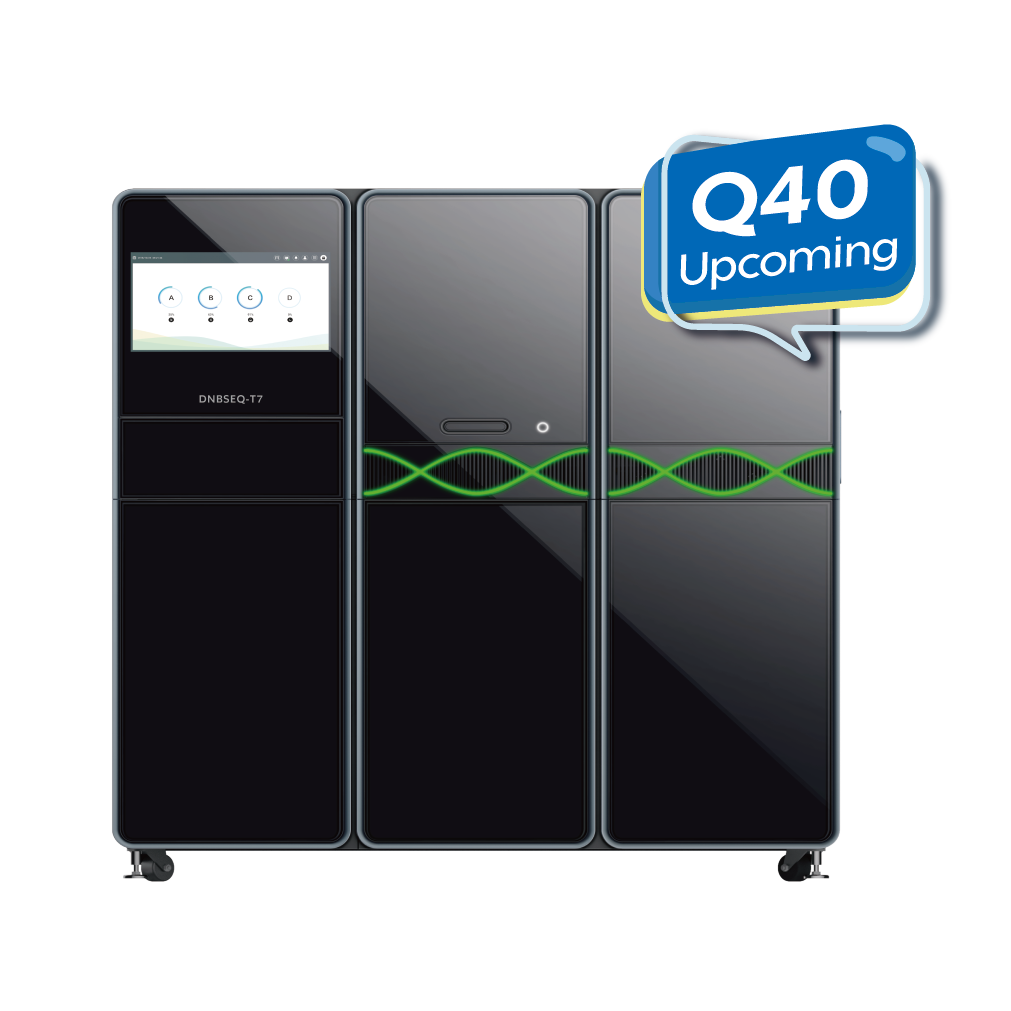
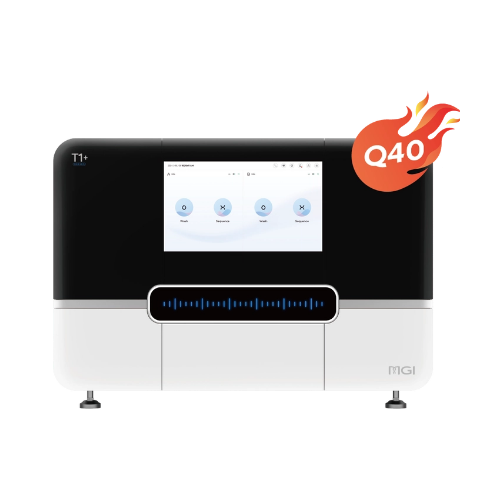
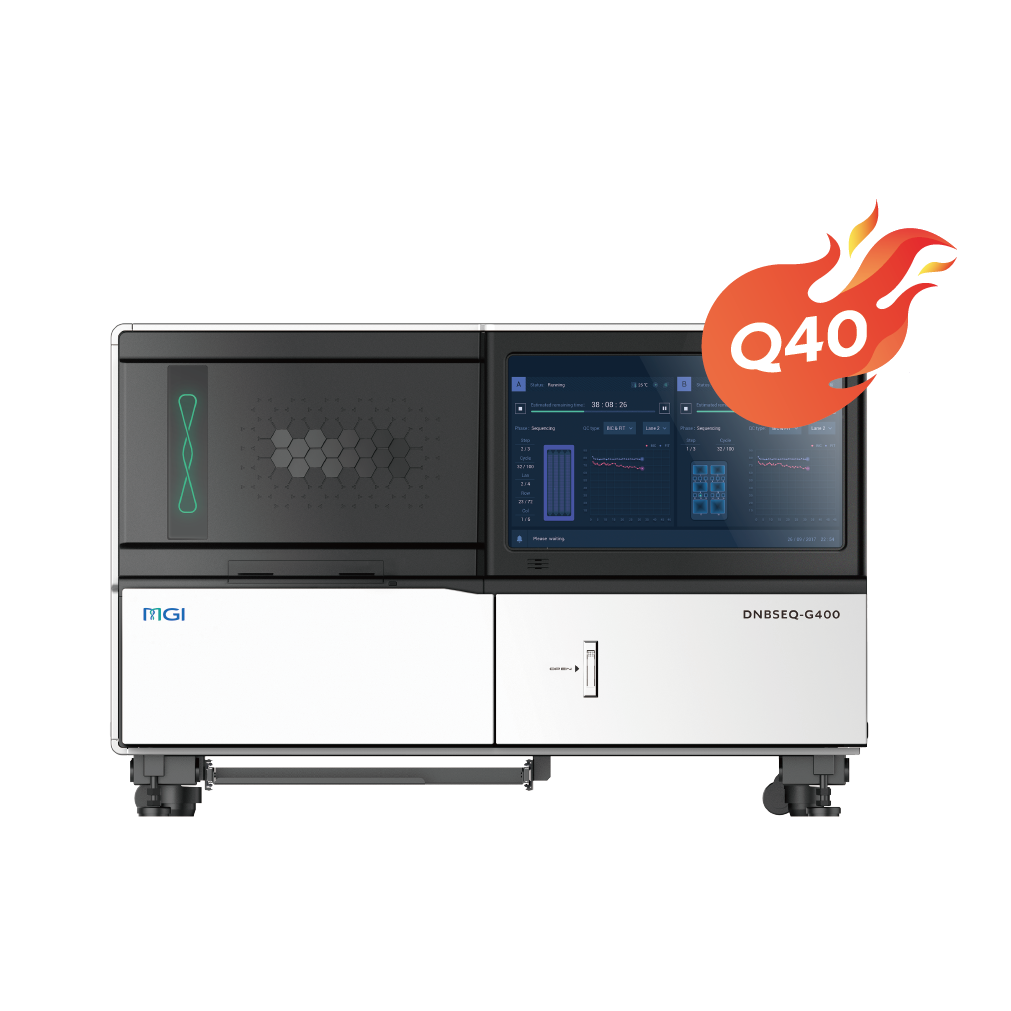
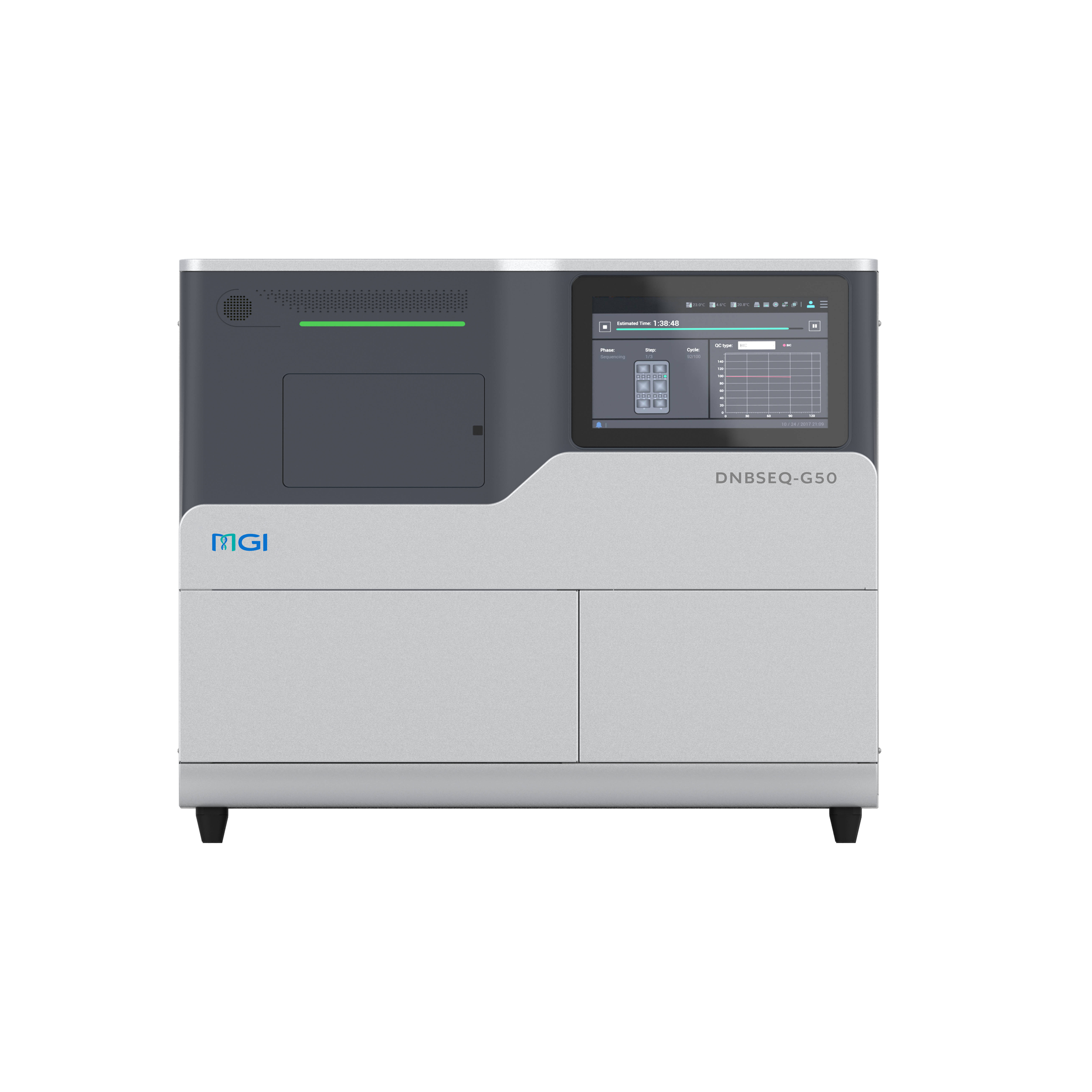
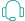
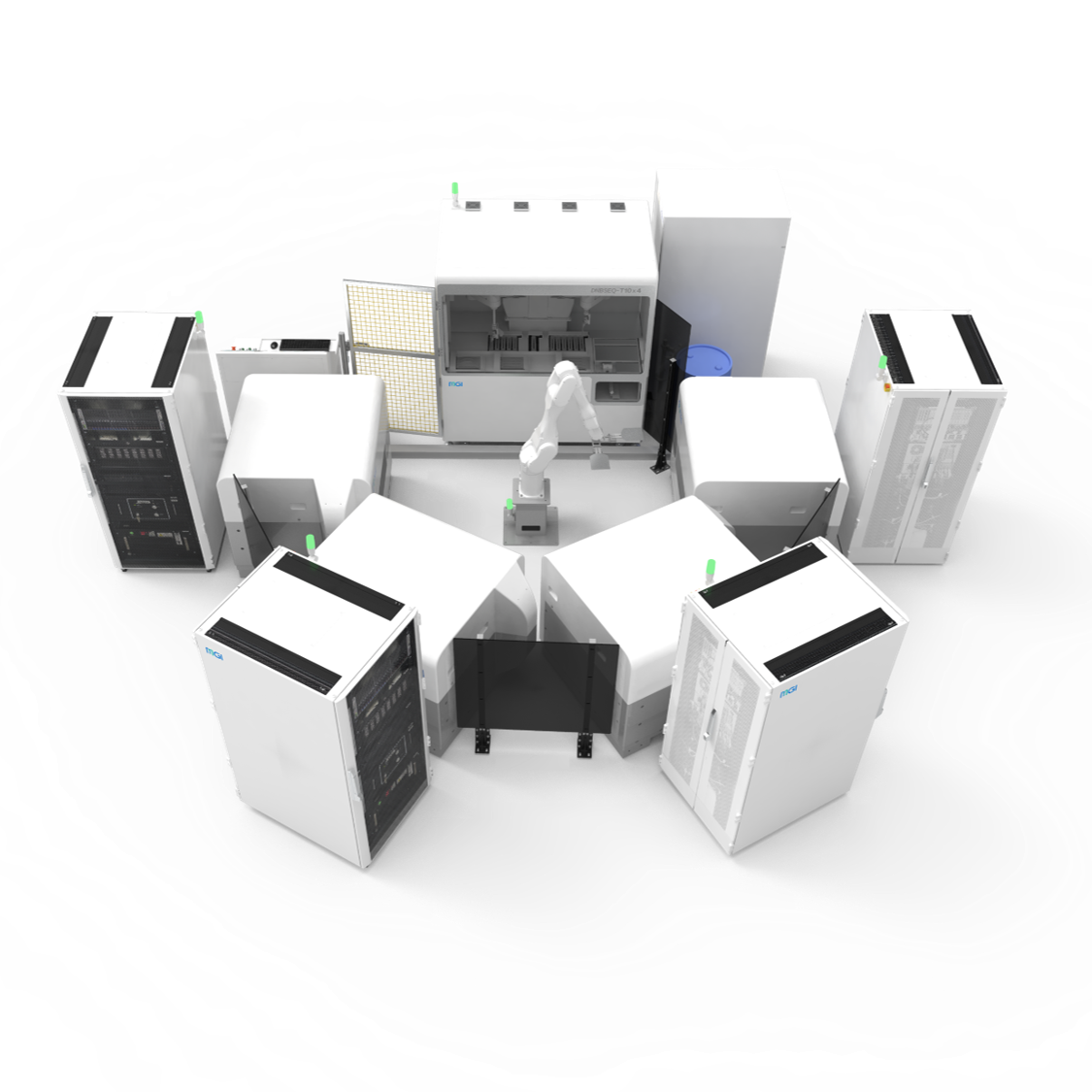
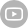
| Product Model | DNBSEQ-T20×2 | DNBSEQ-T10×4RS | DNBSEQ-T7 | DNBSEQ-T1+ | DNBSEQ-G400 | DNBSEQ-G50 | DNBSEQ-G99 | DNBSEQ-E25 |
| Sequencing Quality | Q30>85% (PE150) | Q30>85% (PE150) | Q30>85% (PE150) | Q30>93% Q40>90% (PE150) | Q30>85% Q40>85% (PE150) | Q30>80% (PE150) | Q30>90% Q40>85% (PE150, SM 2.0) | Q30>80% (PE150) |
| Dimensions | 4200 mm *4800 mm *2000 mm | 7200 mm *5000 mm *1950 mm | 1656 mm *903 mm *1815 mm | 1150 mm*816 mm*750 mm | 1086 mm *756 mm *710 mm | 654 mm *489 mm *545 mm | 607 mm *680 mm *640 mm | 348 mm *312 mm *257 mm |
| Applications | Ultra-high-depth Whole Genome Sequencing | Ultra-high-depth Whole Genome Sequencing | Deep Whole Genome Sequencing | Oncology panel sequencing, WGS, WES, WGBS, etc. | WGS, WES, Transcriptome sequencing, etc. | Small whole genome sequencing, targeted panels, low-pass whole genome sequencing | Targeted oncology panel sequencing, infectious disease sequencing, 16S Metagenomic Sequencing | Rapid Identification of Pathogenic Microorganisms, Small whole genome sequencing, targeted panels |
| Max. Flow Cell / Run | 6 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Flow Cell Type | Slide | Slide | FC | FCS & FCM & FCL | FCS & FCL | FCS & FCL | FCS & FCL & FCU | FCL |
| Lane/Flow Cell++ | 1 Lane | 1 Lane | 1 Lane | 2 Lanes & 4 Lanes & 4 Lanes | 2 Lanes & 4 Lanes | 1 Lane | 1 Lane | 1 Lane |
| Operation Mode | Ultra-high throughput | Ultra-high throughput | High Throughput | Medium and High Throughput | Medium and High Throughput | Medium Throughput | Low and Medium Throughput | Low throughput |
| Max. Throughput / Run | ~72 Tb | 76.8 Tb | 7 Tb | 1.2 Tb | 1440 Gb | 150 Gb | 240 Gb | 7.5 Gb |
| Effective Reads / Flow Cell | 40 B | 32 B (PE150) | 5800 M | 500 M, 1000 M, 2000 M | 300 M, 550 M, 1500 M~1800 M | 100 M, 500 M | 40 M, 80 M, 200 M | 25 M |
| Average Run Time | 60 hrs~80 hrs | 96 hrs~106 hrs | 16 hrs~24 hrs | FCS: 4.5 hrs~35 hrs FCM: 6 hrs ~19.5 hrs FCL: 7 hrs ~24 hrs | FCS: 13 hrs~37 hrs FCL: 14 hrs~109 hrs | 7 hrs~40 hrs | FCS: 11 hrs FCL: 5 hrs~30 hrs FCU: 7 hrs~35 hrs | 5 hrs~20 hrs |
| Min. Read Length | PE100 | PE100 | PE100 | SE50 | SE50 | SE50 | SE100 | SE100 |
| Max. Read Length | PE150 | PE150 | PE150 | PE300 | PE300 | PE150 | PE300 | PE150 |
>


 Sequencer Products: SEQ ALL
Sequencer Products: SEQ ALL










 Technologies
Technologies Applications
Applications Online Resources
Online Resources Data Bulletins
Data Bulletins Service & Support
Service & Support Introduction
Introduction Newsroom
Newsroom Doing Business With Us
Doing Business With Us Creative Club
Creative Club